Configurations Introduction
Developing comprehensive workflows often requires creating multiple variations of the same workflow with different configuration options. For instance, you might need to run a workflow using different AI models, prompts, or other model parameters. Workflow Configurations provide a streamlined way to define and manage these settings, either through a Configuration UI or a configuration file. These configurations integrate seamlessly into your task implementation, allowing workflows to run with varied settings and supporting experimentation.
Creating Configurations
We offer two methods for creating configurations for your workflow:
Using the Configuration UI
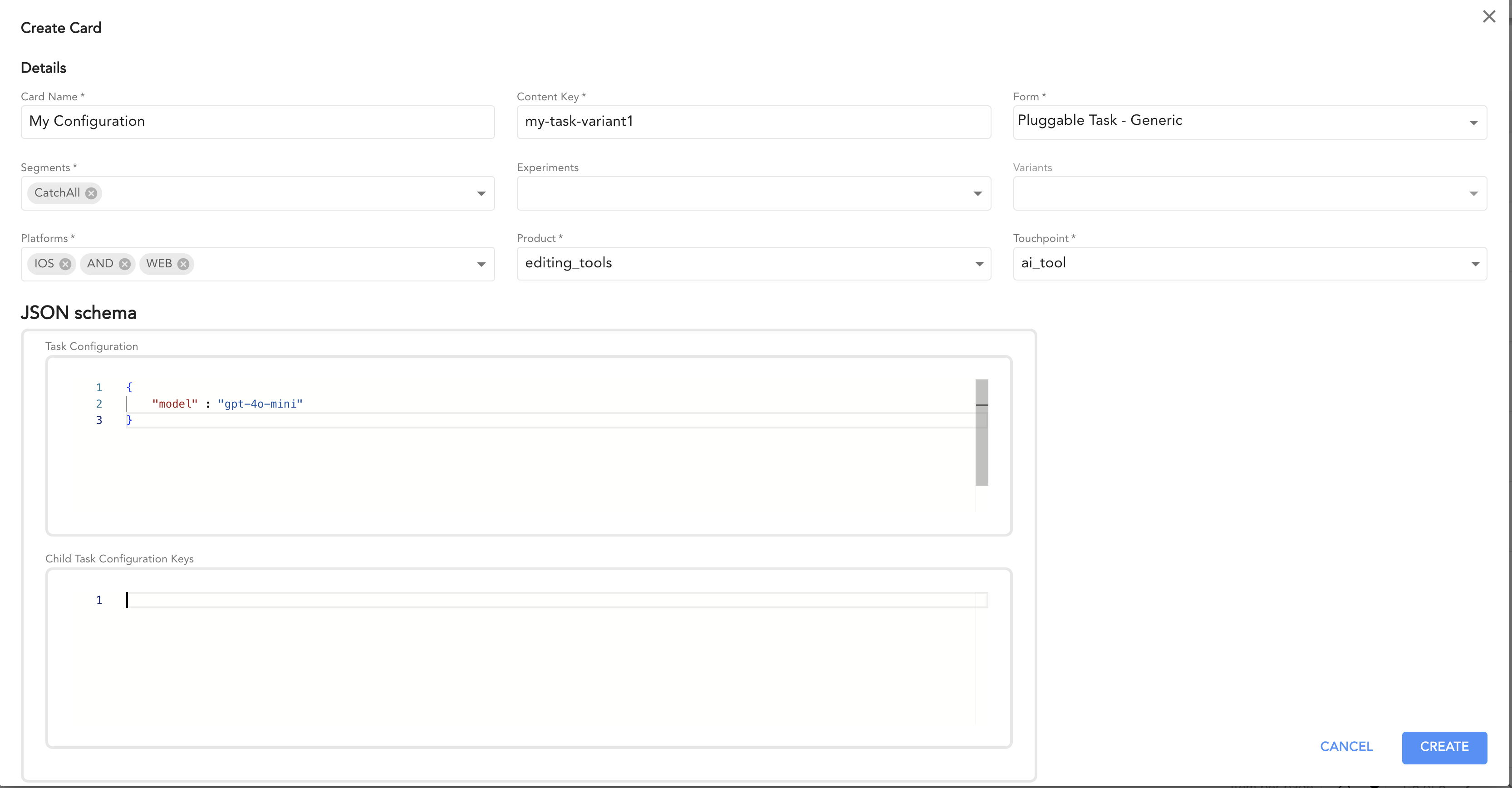
- Navigate to the CMS Cards page and click Create Card.
- Enter a name for your configuration.
- Provide a unique ID in the Content Key field (e.g.,
example-task-variant1). - Select Pluggable Task Generic Form as the form type.
- You can also create a custom form. Learn more here.
- Add your task's JSON configuration in the Config field. Example:
Using a Config File in the Worker Repository
- Create a configuration file at the following path:
src/config/tasks/{task-executor-name}.yaml
When defining versioned task executors, use the same path, but replace all / characters in the task name with - to form the file name.
Examples
| Task executor name | Configuration file path |
|---|---|
example-task/v1 | src/config/tasks/example-task-v1.yaml |
ideogram/photo/realistic/v2 | src/config/tasks/ideogram-photo-realistic-v2.yaml |
photo/gemini/resize/high | src/config/tasks/photo-gemini-resize-high.yaml |
- Add your configuration, using the configuration ID as the key. Example:
example-task-variant1:
config:
model: gpt-4o-mini
example-group-v2-example-task:
config:
model: gpt-4o-pro
The default configuration key follows the pattern {task-executor-name}-default. For example, for a task named
example-task, the configuration would be:
example-task-default:
config:
model: gpt-4o-mini
Accessing Configurations in Your Task Executor
You can retrieve the configuration within your task implementation using the flow.config object. Here's an example
@Executor("example-task")
export class ExampleExecutor implements TaskExecutor {
async processTask(
exampleCommand: ExampleCommand,
meta: TaskMetadata,
flow: Flow
): Promise<ExampleResponse> {
// Retrieve the configuration
const config = await flow.config.get();
// Use the configuration in the response
return {
result: `Using model ${config.model} !!!`
};
}
}
API
When calling to Workflows API you can choose the desired configuration by passing x-config-id header.
Example:
curl --location '$HOST/workflows/example-workflow/submit' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'x-config-id: example-task-variant1' \
--data '{
"params": {
}
}'
Subtask Configuration
When building workflows, you may need to configure not only the top-level task but also any nested subtasks it triggers. Subtask configuration enables fine-grained control over each nested task's behavior while preserving a clear, hierarchical structure.
This approach makes it easy to reuse task implementations with different settings and allows parent tasks to dynamically influence their subtasks.
Defining Subtask Configuration
You can specify subtask configurations using the subTasks field in your configuration file. The value must be a config Id
For example:
ideogram:
config:
model: V_2_TURBO
subTasks:
text2image: text2image-ideogram
ideogramis the main task.- The
subTasksfield must be a config ID, referencing the subtask to be called by this task. text2imageis the identifier for a nested task its value, id, references a specific configuration ID of the text2image task that should be used when it's triggered byideogram
Corresponding configuration in the text2image worker:
text2image-ideogram:
config:
modelVersion: PHOTOREALISTIC
Default Subtask Behavior
If you do not specify a subtask under subTasks, the system will automatically use the default subtask for the command, named as {commandName}-default.
This makes it easy to extend or override default behavior by simply adding or omitting the subTasks field in your configuration.